Advancing regenerative agriculture through the Green Transformation Pathways Project
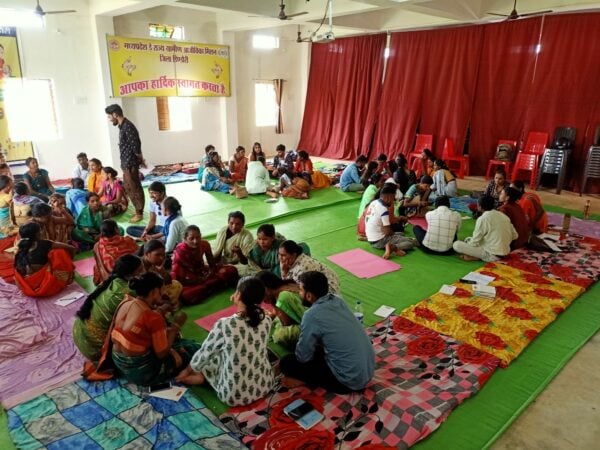
Article by Marina Vara Gutiérrez (Regenerative Agriculture expert at AidEnvironment) What a journey it is being part of the Green Transformation Pathways (GTP) project in India! The GTP project is rooted in four pillars: regenerative agriculture, natural resources management, local economy, and women’s centrality. In September 2023, as part of the regenerative agriculture workstream developed for the project, Ruben Borge […]
Read more